
Explore 4.29 The Early History of Life, to Fishes
Learning Objectives
By the time you have completed the 4.29. Introduction & Exploration Activities, you should be able to:
- Describe the differences between direct divine creation (natural) and lawful creation (through lawful self-assembly) -- especially how each explains the development of life.
- Understand that observations suggest that natural processes produced the first cells.
- Identify examples of the lawful body molding that produced complex fishes (with lobed fins and lungs) from early simple fishes (that lacked teeth, jaws, bony skeletons and lungs).
Development of Life
Describe the differences between natural theology explanations and lawful self-assembly explanations of the development of life.
Natural Theology
God created in the Universe “worlds without number.”
Lawful Self-Assembly
Natural Theology
God created the Earth with ‘matter unorganized.”
Lawful Self-Assembly
Natural Theology
God created the dry land by separating the land from the sea.
Lawful Self-Assembly
Natural Theology
God created all life within its own sphere.
Lawful Self-Assembly
Lawful First Cells
Understand that observations suggest that the first cells arose lawfully via natural processes; for example, observations that biological molecules (e.g., amino acids), replicating systems (e.g., RNA), and structures (e.g., cell membranes) self-assemble under conditions such as those on early Earth.
Include the images under Life Forms from the previous explore 5.1 Question: What are the processes that must happen in order for life to arise lawfully via natural processes? Answer: 1. The formation of biomolecules 2. Chemical evolution 3. Development of protocells 4. Development of the genetic code. Include the figure of the drawing of the Bacteria and Archaea tree and where they intersect. Question: What does this figure indicate about the relationship between Bacteria and Archaea and the formation of eukaryotic cells? Answer: Symbiotic relationships developed between prokaryote species (from Bacteria and Archaea)—producing the first complex single cells (eukaryotes). The cells of both animals and plants (eukaryotes) are comprised of the symbiotic descendants of simple prokaryote cells.
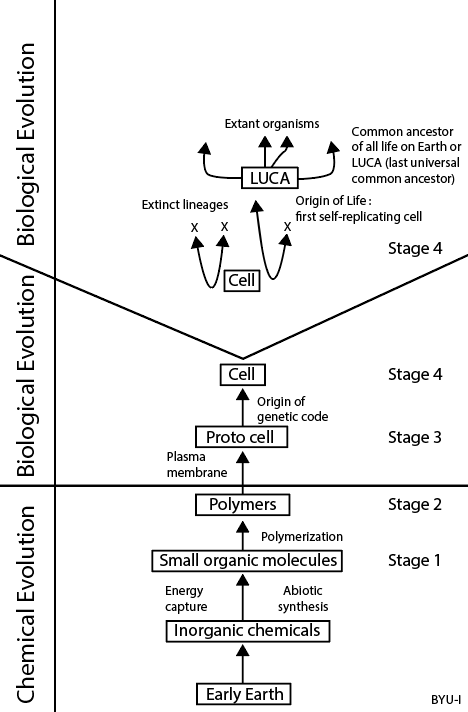
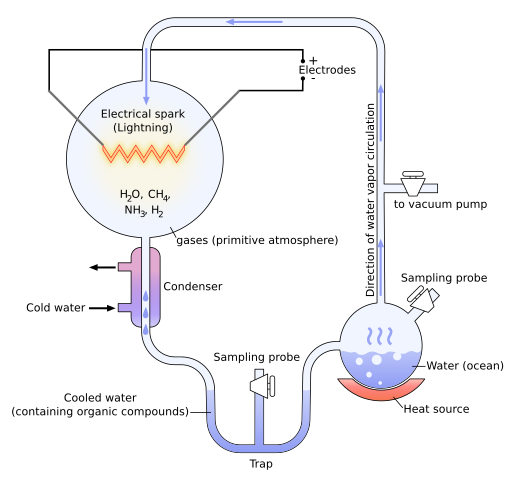
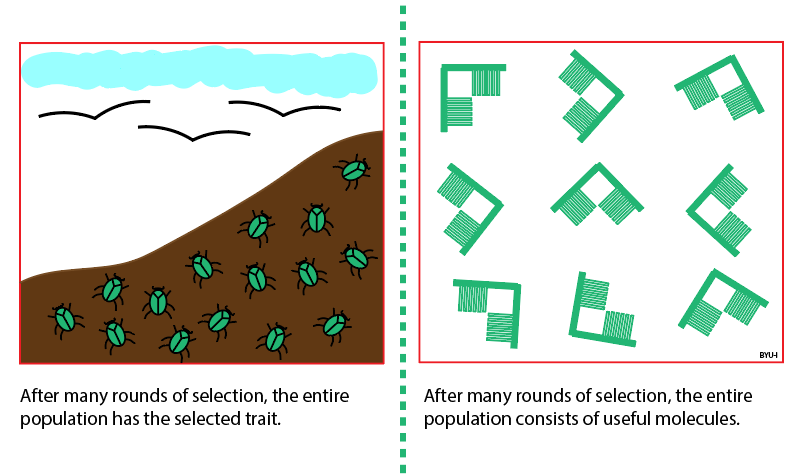
What are the processes that must happen in order for life to arise lawfully via natural processes?
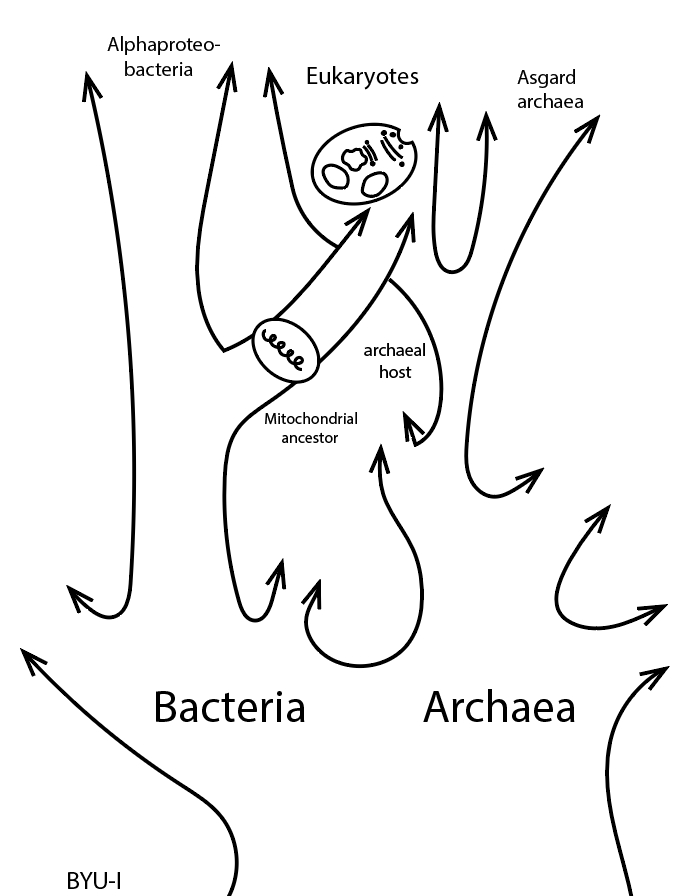
What does this figure indicate about the relationship between Bacteria and Archaea and the formation of eukaryotic cells?
Transitions of States
Identify the basic innovations [new feature(s)] that characterize the transitions between the following states/stages/body forms: early jawless fish to jawed fishes to bony fishes to lobe-finned fishes with lungs. Also, describe how genetic innovation and the feedback between embryological development and natural selection molds the characteristics of organisms through time and produces new species.
The Hagfish Is the Slimy Sea Creature of Your Nightmares